Adult gypsy moth food
 Female Gypsy moths cannot fly. He had intentionally brought it to his home in Massachusetts, from France, to study the insect with an interest in silk production. While in the larval stage, the gypsy moth might be confused with fall webworms or eastern tent caterpillars. Forest Insect and Disease: This site is for use by municipal forestry departments, park districts, the green industry and other concerned agencies to report gypsy moth findings in NortheasternIllinois. Integrated Pest Management Manual.
Female Gypsy moths cannot fly. He had intentionally brought it to his home in Massachusetts, from France, to study the insect with an interest in silk production. While in the larval stage, the gypsy moth might be confused with fall webworms or eastern tent caterpillars. Forest Insect and Disease: This site is for use by municipal forestry departments, park districts, the green industry and other concerned agencies to report gypsy moth findings in NortheasternIllinois. Integrated Pest Management Manual..gif)
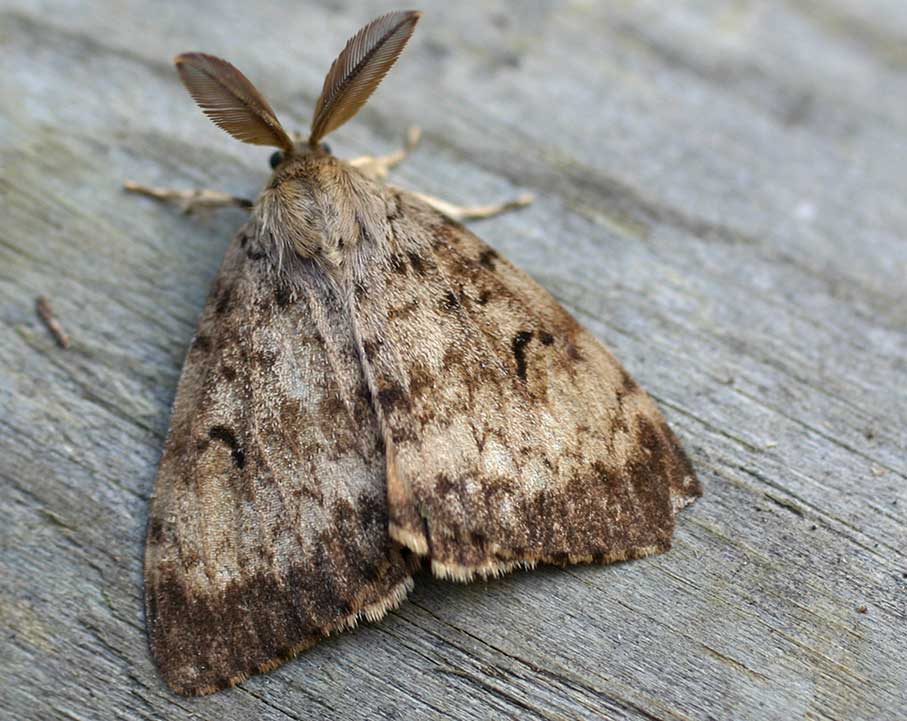





What Do Gypsy Moths Eat?
 It is at this stage that people usually begin to notice the caterpillars and the defoliation of trees. A population of gypsy moths will exist for many years in low densities. Damage This key pest is indirectly responsible for causing mortality of susceptible host trees. On the other hand, avian predation and invertebrate predation show only small effects on the population dynamics of the gypsy moth. Many people experience allergy-type reactions to these hairs. Secondary organisms such as the twolined chestnut borer, Agrilus bilineatus , and shoestring root rot, Armillaria spp. Experiments indicate that known gypsy moth pathogens and gypsy moth bodily fluid negatively affect the survival of swallowtail larvae.
It is at this stage that people usually begin to notice the caterpillars and the defoliation of trees. A population of gypsy moths will exist for many years in low densities. Damage This key pest is indirectly responsible for causing mortality of susceptible host trees. On the other hand, avian predation and invertebrate predation show only small effects on the population dynamics of the gypsy moth. Many people experience allergy-type reactions to these hairs. Secondary organisms such as the twolined chestnut borer, Agrilus bilineatus , and shoestring root rot, Armillaria spp. Experiments indicate that known gypsy moth pathogens and gypsy moth bodily fluid negatively affect the survival of swallowtail larvae.


Gypsy Moth | Center for Agriculture, Food and the Environment UMass Amherst
The tiny caterpillars hang in the air waiting for a strong wind to break the thread and carry them to a new location. Even though numerous chemical pesticides are available, it is best to manage problematic populations of this pest early and utilize B. Wear gloves and protect exposed skin from the egg masses while removing them. The adult of this beetle eats gypsy moth larvae, and the larval beetles seek out and feed on the moth pupae.






Gypsy Moths

Description: During the late s and early ls the leading edge of the infestation advanced into Centre, Blair, Huntingdon and Clearfield Counties. Wrapping trees with burlap folded over a cord to entrap caterpillars seeking shelter during the day is also ineffective due to the scope of the problem. Once hatched, the tiny, hairy caterpillars may remain in the lower forest canopy or, when in high populations, migrate upwards to the tree tops, where each one then spins down on a long silken thread. Thinning of forests by gypsy moths may produce a healthier, more diverse, and perhaps a more gypsy-moth resistant stand of trees. The pupal stage is dark reddish-brown and is held in place to some object by small strands of silk.
Views: 2711
Date: 11.02.2016
Favorited: 5
























.jpg)










User Comments
Post a comment
Comment: